Page 93 - TheTalents 2018 Debate2
P. 93
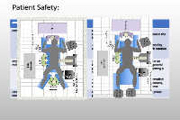
Patient Safety:
Anesthetic Consideration
Intraocular pressure: Improved in Supine position
NO reported cases of post anesthetic visual loss in the
• Improved parameters for high risk patients:
• Reduced intraocular pressure
• Increase HR, decrease BP, dec cardiac index, decrease venous return due to
literature for PCNL
-elevated intraocular pressures can be mitigated by
using a prone helmet, rather than lateral neck rotation thoracic pressure, increase peak pressures
• “...patients with marginal heart and lung function do not tolerate the prone position well.”
Improved Functional Capacity, Compression of IV and Those with severely compromised FEV1 have a 5x reduction of preload higher risk of cardiovascular death then the general
• Patients with a severely impaired FEV1 have a 5x increased risk of
population. This patient population is likely getting a
cardiovascular death at baseline. Therefore this population would be high
risk for any surgery/complication.
staged ureteroscopy or ‘observation’
-Pressure controlled ventilation > Volume controlled ventilation improves peak and plateaued pressures, oxygenation and reduces stress/cortisol reponse
Decreases the number of times re-positioned after anesthetized
Can perform retrograde contrast, or ECIRS in prone patients by simply splitting the legs